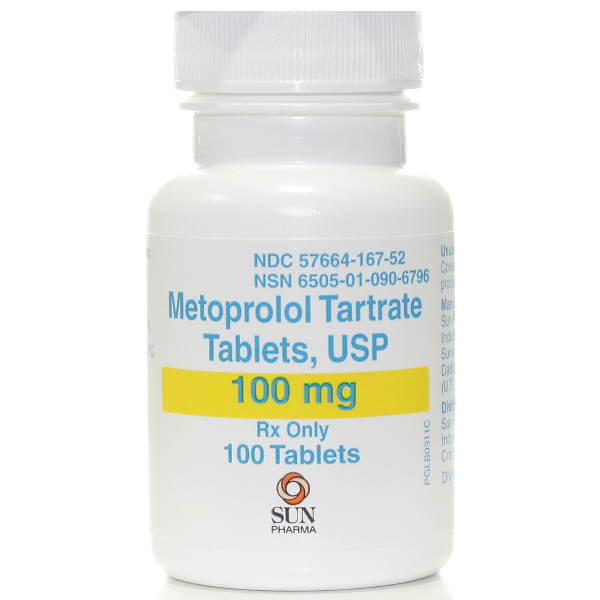
📌 Medicine Name:
Metoprolol Tablet 100 mg
(Available as Metoprolol Tartrate – immediate release, or Metoprolol Succinate – extended release)
📋 Description / Prescription:
Metoprolol is a prescription-only beta-blocker used in the treatment and prevention of several cardiovascular conditions.
🔹 Each tablet contains 100 mg of metoprolol (either as tartrate or succinate).
- Tartrate: short-acting, typically taken twice daily
- Succinate: extended-release, usually taken once daily
🩺 Common Indications:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Chronic stable angina
- Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) – succinate form only
- Atrial fibrillation, tachyarrhythmias
- Post-myocardial infarction (MI)
- Off-label: migraine prevention, thyrotoxicosis symptoms, essential tremor
🔬 Nature / Mechanism of Action:
Metoprolol is a selective β1-adrenergic receptor blocker (cardioselective), which:
- Decreases heart rate, cardiac contractility, and blood pressure
- Reduces myocardial oxygen demand
- Helps control abnormal heart rhythms
✅ Advantages / Therapeutic Benefits:
- ✅ Provides effective BP control, reducing the risk of stroke/MI
- ✅ Prevents and reduces frequency/severity of angina
- ✅ Reduces mortality and hospitalization in heart failure patients
- ✅ Controls ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation
- ✅ Offers symptomatic relief in hyperthyroidism and migraines
📦 Packaging:
- Available as round or oval, film-coated tablets
- May be scored for dose splitting
- Common packaging: blister strips or HDPE bottles
- Pack sizes: 10, 30, 50, or 100 tablets
🌡️ Storage:
- Store at 15–30°C (59–86°F)
- Keep in a dry, cool place, protected from light and moisture
- Keep out of reach of children
⚠️ Precautions:
Use cautiously in patients with:
- Bradycardia or AV block (2nd/3rd degree)
- Asthma or COPD – may worsen bronchospasm
- Diabetes – may mask hypoglycemia symptoms
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Liver dysfunction
🚫 Do not stop suddenly — can cause rebound hypertension, worsening angina, or MI
Drug interactions include:
- Calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem)
- Digoxin
- Clonidine
- NSAIDs (may reduce antihypertensive effect)
👩⚕️ Patient Advice / Counseling Points:
- 💊 Take with or immediately after food to improve absorption
- 🕒 Take at the same time daily, ideally in the morning for once-daily doses
- ❌ Do not stop abruptly—taper slowly under medical supervision
- 🚗 May cause fatigue, dizziness, or drowsiness—use caution while driving
- 🩺 Monitor blood pressure and heart rate regularly
- 📞 Contact your doctor if:
- You feel excessively slow heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling, or cold extremities
- You experience worsening fatigue or mental/mood changes