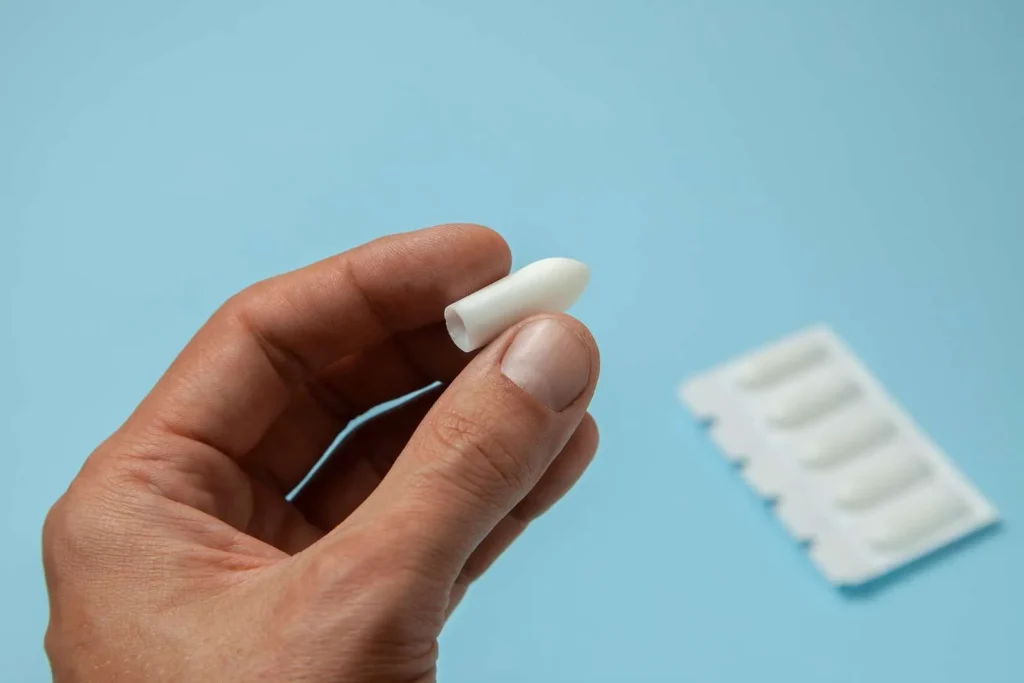
💊 Diazepam Pediatric Suppository 5 mg
📌 1. Prescription / Indication:
Diazepam 5 mg suppository is prescribed primarily for emergency control of seizures, especially in children:
- Status epilepticus (acute seizures)
- Febrile seizures in pediatric patients
- When oral/IV administration is not possible
- Preoperative sedation in select cases
📄 2. Description:
- Form: Rectal suppository
- Strength: 5 mg of Diazepam
- Route: Rectal (PR)
- Prescription status: Schedule H (Rx) – prescription-only medicine
- Appearance: Usually torpedo-shaped, white to off-white solid
🔬 3. Nature / Class:
- Drug Class: Benzodiazepine
- Action:
- Sedative
- Anxiolytic
- Anticonvulsant
- Muscle relaxant
- Mechanism: Enhances GABAergic inhibition in the central nervous system → controls seizures and calms CNS activity
🌟 4. Advantages:
- Quick absorption via rectal mucosa
- Effective during seizures when IV access is difficult
- Useful at home or during transport to hospital
- Pediatric-friendly in emergencies
📦 5. Common Packaging:
| Pack Size | Form |
|---|---|
| 5 mg x 1, 5 mg x 5, or 10 suppositories | Foil strips or blister packs |
🧊 6. Storage Guidelines:
- Store at below 25°C (77°F)
- Protect from moisture and direct sunlight
- Do not freeze
- Keep out of reach of children
👩⚕️ 7. Patient/Caregiver Advice:
- For rectal use only — do not swallow
- Caregiver should:
- Place the child in lateral (side-lying) position
- Insert the suppository gently and fully
- Hold the buttocks together briefly to prevent expulsion
- Observe for:
- Drowsiness
- Breathing difficulty
- Allergic reactions
- Seek medical care immediately after use, especially for seizures
- Do not repeat without medical advice
- Avoid alcohol, opioids, or other sedatives in combination
🎯 8. Purpose / Uses:
- Rapid control of seizures in pediatric patients
- Effective during febrile convulsions
- Used in emergency kits for epilepsy
- In some cases, used for preoperative sedation
⚠️ 9. Warnings / Precautions:
- Risk of respiratory depression
- Use with extreme caution in infants
- Can cause:
- Sedation
- Confusion
- Poor coordination
- Avoid frequent use to prevent dependence or withdrawal