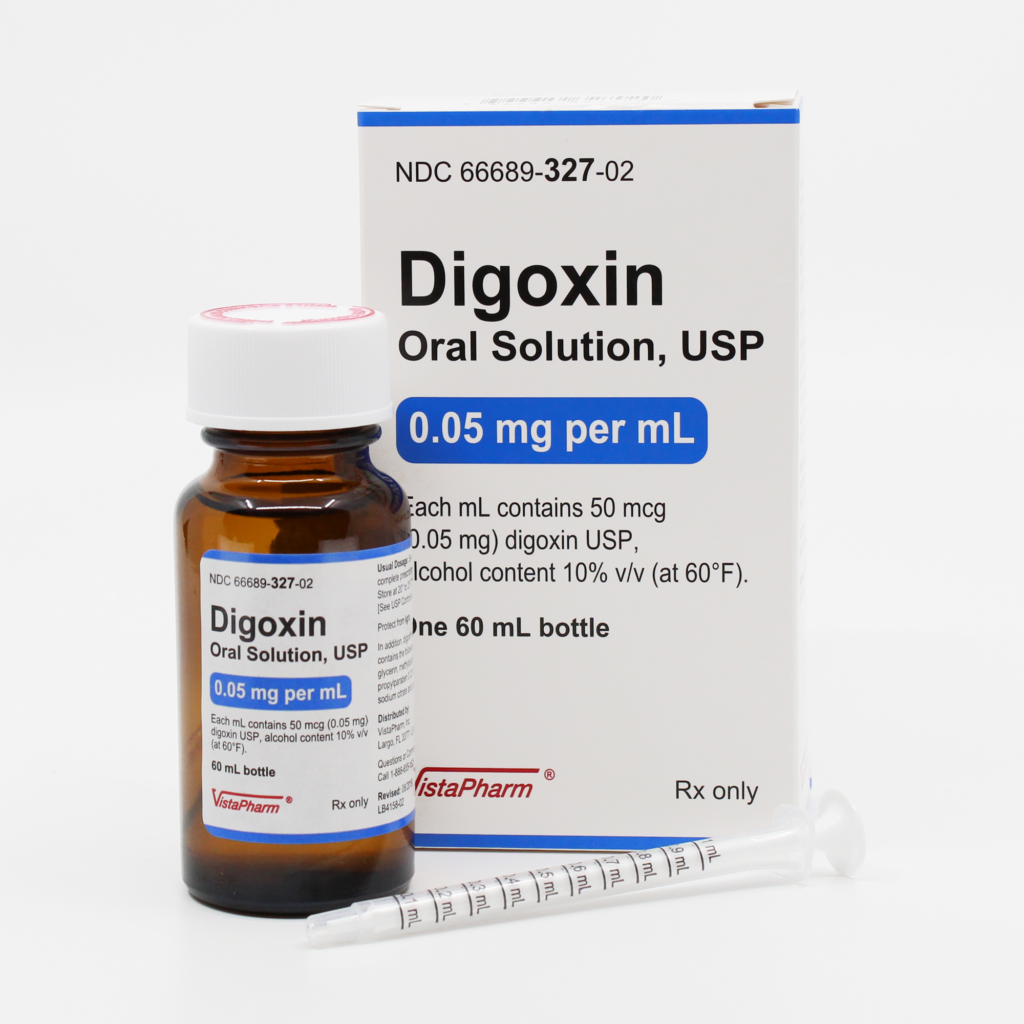
📌 Medicine Name:
Digoxin Oral Liquid 0.05 mg/mL
(Also written as 50 micrograms/mL)
📋 Description / Prescription:
- Type: Cardiac glycoside
- Form: Oral liquid solution
- Strength: 0.05 mg per mL (50 micrograms/mL)
- Route: Oral
- Prescription status: Prescription-only medicine (Rx)
- Use: Heart failure and control of heart rate in certain arrhythmias
🩺 Nature / Mechanism of Action:
Digoxin improves heart function by:
- Inhibiting Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase → increased intracellular calcium
- Enhancing myocardial contractility (positive inotropy)
- Slowing AV nodal conduction, beneficial in atrial arrhythmias
- Increases vagal tone → lowers heart rate
✅ Advantages / Benefits:
- ✅ Allows precise and adjustable dosing, ideal for children and elderly
- ✅ Preferred when tablets are unsuitable (e.g., feeding tubes, swallowing difficulties)
- ✅ Fast absorption and predictable pharmacokinetics
- ✅ Once-daily dosing possible due to long half-life
- ✅ Useful in congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation/flutter
📦 Packaging:
- Supplied in amber-colored bottles (protect from light)
- Common sizes: 30 mL, 60 mL, 100 mL
- Comes with calibrated oral syringe or dropper for accurate dosing
- Often labeled as pediatric solution
🌡️ Storage Instructions:
- Store at 15°C–25°C (59°F–77°F)
- Protect from light and moisture
- Keep tightly closed in original container
- Do not freeze
- Keep out of reach of children
⚠️ Precautions / Warnings:
Do NOT use in:
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Known digoxin allergy
- Severe heart block (without pacemaker)
Use with caution in:
- Elderly patients
- Renal impairment – adjust dose
- Electrolyte imbalances:
- Hypokalemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hypercalcemia
- Thyroid disease (alters digoxin sensitivity)
- Drug interactions: especially amiodarone, verapamil, quinidine, diuretics
⚕️ Common Dosing (example, not for self-use):
| Age Group | Usual Oral Maintenance Dose |
|---|---|
| Adults | 0.125–0.25 mg/day (2.5–5 mL) |
| Children (weight-based) | Adjusted per kg |
✅ Always prescribed by a doctor based on age, weight, kidney function, and clinical condition. Overdose can be fatal.
⚠️ Signs of Toxicity to Watch For:
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite
- Visual disturbances (blurred/yellow vision)
- Confusion, drowsiness
- Irregular or slow heart rate
- In infants: poor feeding, lethargy
👩⚕️ Patient Advice / Counseling Tips:
✅ How to use:
- Use measuring syringe/dropper provided
- Administer at the same time daily
- Give with or without food
- Shake well only if label instructs (some forms do not require shaking)
✅ What to avoid:
- Do not mix with dairy or antacids
- Avoid giving other medications simultaneously (space apart if needed)
- Avoid overdosing — small amounts can be toxic
✅ Inform your doctor if:
- You notice signs of digoxin toxicity
- Your child or elderly patient has vomiting or behavior changes
- There is a change in kidney function or other medications